Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Are DC Motors?
A DC motor is an electric machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy or mechanical rotation. In the working process of DC motors, electrical currents generate a magnetic field that powers the movement of the motor’s rotor.
The Working Principle of DC Motors
The principle behind DC motor operation is based on Lorentz’s Law. This law states that when a current-carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field, it experiences a mechanical force. Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule is used to determine the direction of this force, while the equation F=BILF = BILF=BIL gives its magnitude, where BBB represents magnetic flux density, III is current, and LLL is the length of the conductor in the magnetic field.
To apply this rule to DC motors: by stretching your left hand with the thumb, first, and second fingers perpendicular to each other, the direction of the magnetic field is indicated by the first finger, the direction of the current by the second finger, and the thumb shows the direction of the force experienced by the current-carrying conductor.
The DC motor’s operation begins with a direct current (DC) supply, which generates an electric current through the armature winding. The interaction between this current and the magnetic field produces a force that causes the rotor to turn, resulting in mechanical motion.
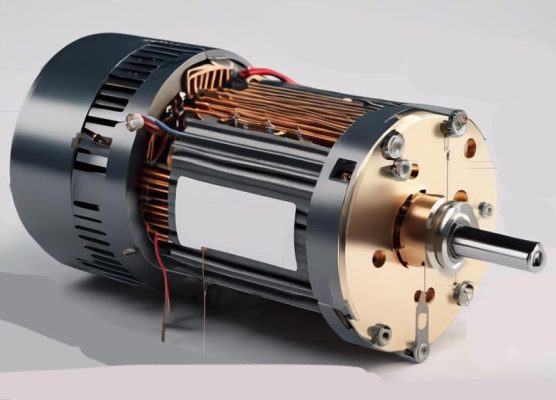
Key Parts of a DC Motor and How They Work
For a DC motor to function effectively, it must have the following components:
- Stator: The stationary part of the motor, which contains the field windings and receives the power supply.
- Rotor: The rotating part of the motor that generates mechanical motion. The rotor’s movement is what drives the motor.
- Yoke: The yoke serves as the protective outer frame of the motor, shielding the internal components and supporting the armature. It also encloses the magnetic poles and field windings, helping to maintain the motor’s structure.
- Magnetic Poles: The magnetic poles consist of two main parts: the pole core and the pole shoe. The pole core holds the pole shoe in place, while the pole shoe has slots for the field windings and spreads the magnetic flux into the air gap between the rotor and stator.
- Field Windings: These windings are wrapped around the pole shoes and form an electromagnet when powered. The field windings produce the magnetic field that interacts with the armature to create motion.
- Armature Windings: The armature windings are connected to the rotor and play a crucial role in altering the magnetic field as the rotor moves. To reduce energy loss, the armature core is laminated with low-hysteresis silicon steel.
- Commutator: The commutator is made up of copper segments and is connected to the armature. Its purpose is to transfer current to the armature windings while controlling the direction of the electromagnetic field and torque, allowing for continuous rotation in a unidirectional manner.
- Brushes: Brushes are typically made of carbon or graphite and are in contact with the commutator. They transfer electrical current from the power source to the armature, completing the electrical circuit and enabling the motor to function.
Conclusion
DC motors are essential in numerous applications, from powering small household appliances to driving industrial machinery. By understanding how DC motors work and the function of their key components, it’s easier to grasp their importance in modern technology. These motors are highly efficient, and reliable, and offer great flexibility in speed control, making them suitable for a wide range of uses.
0
